The growth of the economy of Kazakhstan in the first quarter of 2019 slowed slightly to 3.8% yoy from 4.1% yoy in 2018 and was within the government's forecast for the entire current year. As the oil output set to decline due to technical works at the country's largest fields, it can be expected that the economy will also slow down in the second quarter. In this environment, the increase in government spending aimed at increasing the incomes of the population supports the growth of activity in the non-primary sector via increased consumption.
The price of oil throughout the entire first quarter was rising steadily, adjusting after slump at the end of 2018 to $50 per barrel, and exceeds $70 per barrel currently. The rapid recovery in oil prices nevertheless was not accompanied by a concomitant movement in the exchange rate, which was at the peaks near the mark of 380 per US dollar and 5.9 per ruble, once again demonstrating the high flexibility of the national currency in the toward weakening rather than to strengthening. Considering that $70 per barrel is a relatively large burden for the global economy, which is expected to slow down this year, the impulses for growth of the Kazakhstan economy from oil prices and the oil-producing sector are limited.
The situation with the incomes of the population improved in 2018, the share of income in GDP increased to 34.1% from 33.9% in 2017. However, based on the components, the incomes of the population show a negative trend – the share of income from employment fell to a minimum of 63.3% in total income, income from self-employment and entrepreneurship did not change, as a result, the share of income from pensions sharply increased to 18.3% It should be noted that, taking into account those employed in the public sector and national holdings, we estimate that together with pensions and benefits, about 40% of household’s income come from public sector, which is about 5pp higher than before the fall in oil prices in 2014.
The reduction in the share of income from employment suggests that there are significant problems for the development of the non-primary sector, and the decision to raise the minimum wage stresses that private business is struggling because of which wages have not grown in recent years. As a result, it can be concluded that a fairly good economic growth in Kazakhstan in the past 2 years has not transformed into real wages growth that led, among other things, to the usage of funds of the National Fund and engage the mechanisms of non-market administrative measures to suppress inflation to improve the well-being of the population.
The increase of minimum wages, pensions in combination with double-digit real growth in consumer lending, mortgage subsidies from the state stimulate consumer activity at the same level as last year. The growth of retail trade was higher than 6% in annual terms in March 2019.
The labor market showed an increase in demand for labor force, the number of employees rose to the highest level in the entire history of 8.8 million. At the same time, the growth of nominal wages reached 10% yoy, but revenues from the individual income tax in the budget show a negative growth, which raises the question – whether wages are rising in reality.
Investment growth in the first quarter of 2018 remained at a high level of 7% yoy, but half of all investments went into oil and gas production, while in the manufacturing industry investments fell by almost 50% yoy.
Another increase in expenditures of the consolidated budget by 2.8pp to 23.4% of GDP, according to our estimates, will again increase the deficit of the consolidated budget, which has been observed for the fifth consecutive year. In addition to the National Fund, the use of extra-budgetary funds (NBRK, ENPF) is increasing, as a result, the consolidated budget can come to balance only by 2021, if external conditions will remain favorable. In the first quarter, there was an excess of receipts of funds to the National Fund over its use, overall for the year the fund's assets will increase only slightly.
In the first quarter of 2019, inflation slowed to 4.8% from 6.6% a year earlier. Inflation continue to ignore a strong inflation background: the impact of a weak tenge, a high level of inflationary expectations of the population, stimulating fiscal policy, thereby creating an accumulation of risks, especially as a result of the transition of monetary policy to softening.
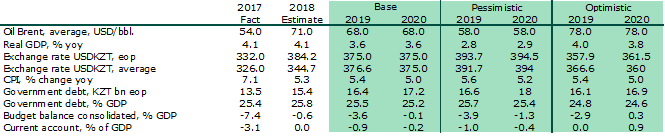
During the first three months of this year, the base rate of the regulator remained unchanged at 9.25% with a discount window +/- 1%. Inflation risks of importing inflation from the Russian Federation and uncertainty in the energy markets were considered by the regulator as potential risks of inflation in the republic. In April, the regulator decided to cut the base rate to 9.0%. It is also necessary to understand that economic growth in 2019, according to our forecast, will slow down to 3.6%, and in such conditions it becomes obvious that in order to maintain economic growth, its growth must be stimulated both through a fiscal stimulus and through easing of monetary conditions. The reduction of the base rate, by definition of the regulator, kept the monetary conditions in the country at a neutral level. However, we believe that through lowering the base rate and supporting economic growth (the NBK has somewhat expanded its mandate), the regulator sends a clear signal to the market that it intends to move precisely towards easing its monetary policy. Our current forecast for the base rate of the regulator at the end of the year is 8.75%.
In March of this year, the new leadership of the National Bank under E. Dosayev made a statement about the continuity of the macroeconomic policy pursued jointly with the government of the republic. The NBK made a statement that it will provide stability in the FX market and has all the necessary tools to prevent speculative transactions with the tenge exchange rate.The continuity of the policy in terms of the exchange rate of the national currency also implies the preservation of its “free floating” regime.
Despite of the high level of energy prices and strengthening of USDRUB, the national currency is at stable “weak” level to eliminate currency arbitrage, to provide favorable conditions for export-oriented companies, as well as to manage trade deficit with the main countries-trading partners. Such an approach in terms of rate is forecasted by us until the end of this year, provided that the current geopolitical and macroeconomic situation in the world remains.
The exchange rate of the national currency against the US dollar will vary within a narrow range of values of 374 tenge (support line) and 385 tenge (resistance line). According to the results of the current forecast round, our annual forecast for the USDKZT pair is 375 tenge per dollar at the end of the year and 376.5 tenge on average for the period.
Exports from Kazakhstan in January-February 2019, according to the preliminary data of the Committee on Statistics, showed rapid growth rates (+ 11.1% yoy) and amounted to $ 9.9 billion compared with imports (+ 0.3% yoy), the volume of which amounted to $ 4.5bn. In the first two months of the year foreign trade turnover increased by 7.5% yoy and amounted to $ 14.3bn.
Analysis of the exports structure from Kazakhstan showed that in January-February 2019, the share of mineral products increased from 71.7% a year earlier to 74.7%. In nominal terms, exports of mineral products grew by 15.9% yoy and amounted to $ 7.4 bn. According to the Committee for Revenue of the Republic of Kazakhstan, in January-February 2019, exports of crude oil and gas condensate grew by 18.7% yoy and amounted to 12.4 million tons. In nominal terms, this export increased by 16.6% to $ 5.9 bn.
An analysis of imports, according to the Statistics Committee, showed that within two months in 2019, Kazakhstan increased imports of machinery, equipment, vehicles, instruments and devices by 2.0% yoy in nominal terms to $ 1.7 billion (the share of imports increased from 37.8% in January – February 2018 to 38.5% in the same period of the current year. We associate the increase in equipment imports primarily with the maintenance works scheduled for March-April at the largest oil fields in the republic. The major part of those imports (49%) come from non-CIS countries, mainly China, Italy, Germany, Turkey and South Korea.
Comparing the data of two months of the current year with the annual data of previous years, it can be concluded that the structure of exports and imports as a whole remains relatively stable and highly likely will not suffer radical changes in the period.
Current account balance of the Republic of Kazakhstan in 2018, according to updated data of the NBK, has developed with a deficit of $ 52mn ($5.1bn in 2017). This is the minimum deficit in the last 4 years. The relative indicator of the current account deficit to GDP decreased from -3.1% in 2017 to -0.03% in 2018 (the indicator is calculated on the basis of preliminary GDP data for 2018).
According to an updated statistics of the NBK for 2018, the outflow of financial resources within the financial account amounted to $2.6bn against inflows of $5.5bn in 2017. An analysis of historical data showed that over the past five years there has been an inflow of capital in the republic ($5.5 bn - $9.7bn) in within the financial account, which was replaced by an outflow of $2.6bn in 2018. The relative indicator of the outflow of financial resources within the financial account to GDP increased from -3.4% (inflow) in 2017 to 1.5% (outflow) in 2018. Thus, within the analyzed period, the acquisition of assets by residents within the financial account prevailed over their commitment to non-residents.
Consolidated international reserves in March 2019, according to preliminary data from the NBK, amounted to $86.0bn. The consolidated assets since the beginning of the year amounted to 3.0% or $2.6bn due to the reduction of the reserves of the NBK by 12.6% to $27bn.
KASE index showed uneven growth in the first quarter of this year. Since the beginning of January of this year, the index has changed from 2,293.7p., evidencing growth in the middle of the month, to a minimum value towards the end of the month at 2,243.8p (the minimum for 1 quarter). Subsequently, there was a steady increase in the KASE index, whose figure as of the end of March updated the six-month maximum, reaching 2,461.3 p (+ 7.3% since the beginning of the year). The growth dynamics demonstrated by the index in the current year repeats the dynamics of last year in Q1, when the index reached its maximum of 2,456.3p.
The main external signals for the growth of the developing countries market, including the Kazakhstan stock exchange market, were positive news in the framework of trade negotiations between Beijing and Washington, as well as news from the US Federal Reserve about the suspension of the increase in the short-term rate, which remained at the level of December 2018 and amounted to 2.50%.